Managing User Access (Clusters)
This topic covers the management of user access to the Kubernetes clusters that Wayfinder manages and is applicable to Wayfinder's administrators as well as the workspace owners. The difference between the two is:
- Wayfinder's administrators manage user access globally for all workspaces.
- Workspace owners manage user access in their workspaces only.
Wayfinder uses its own RBAC implementation to provide access to the Kubernetes clusters that Wayfinders manages. These RBAC concepts are similar to Kubernetes' native RBAC concepts of Groups, Roles, Role Bindings and Access Policies, but you should familiarise yourself with Wayfinders implementation as outlined in this topic.
The diagram below illustrates access to Wayfinder itself (left hand side of the diagram) and access to the Kubernetes clusters that Wayfinder manages (RBAC) (right hand side of the diagram).
This topic covers the right-hand side of the diagram:
- The same set of workspace groups that grant access to Wayfinder itself is also used to provide access to the clusters that Wayfinder manages.
- Roles permit permissions against Kubernetes resources
- Access Policies constrain a role's permitted permissions to specific resources and conditions
- Wayfinder ships with a global set of roles, rolebindings, access policies and workspace groups which all workspaces inherit by default. These are managed internally by Wayfinder and are read-only within workspaces, but can be disabled at the platfrom-level. Wayfinder administrators and workspace owners add users to the respective workspace groups.
- Wayfinder administrators and workspace owners can optionally create custom roles, rolebindings, access policies and workspace groups which only exist and operate in the workspace in which they have been created. These can be deleted and updated as they are specific to the workspace in which they have been created.
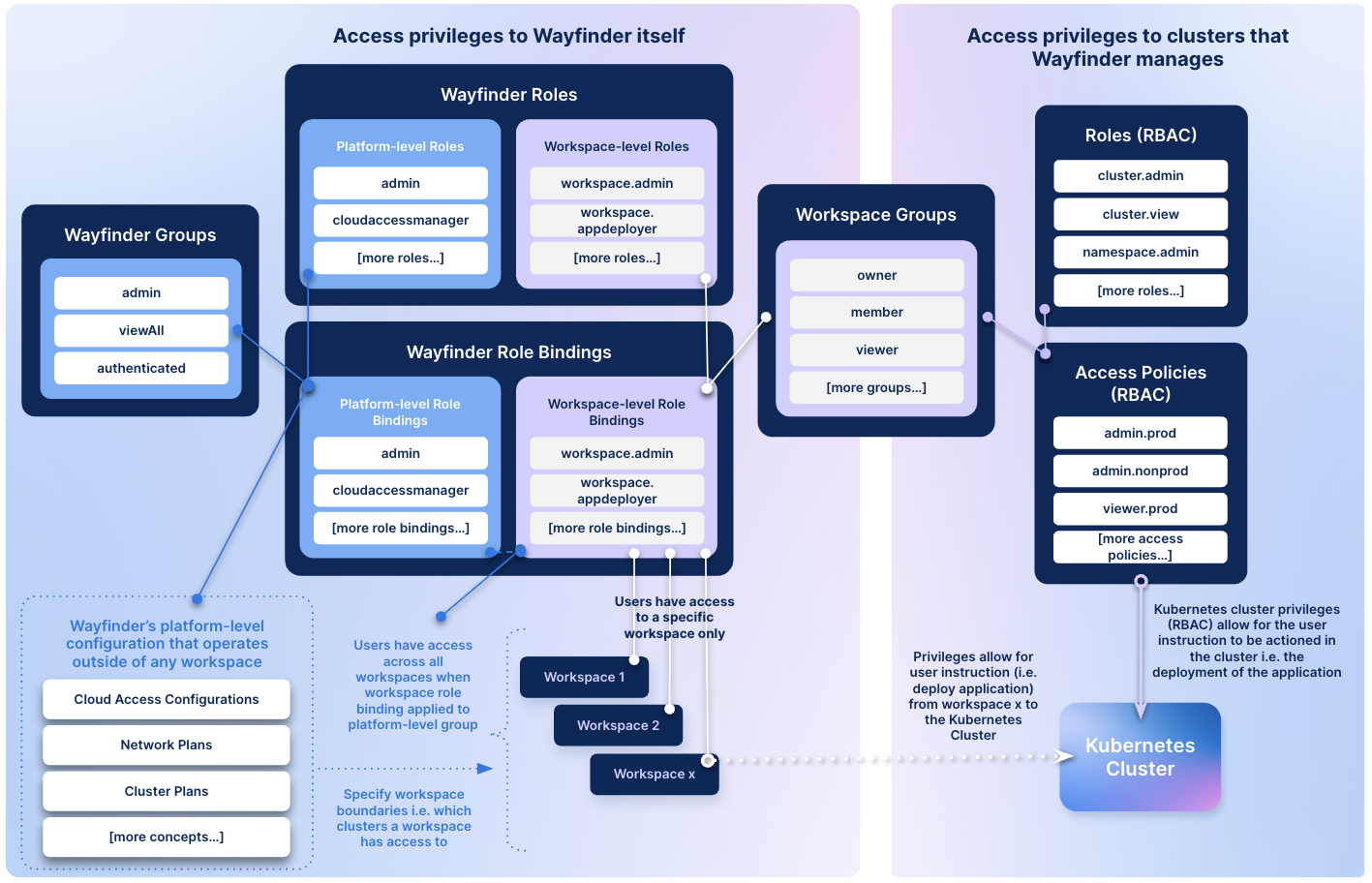
Left hand side of the diagram: (Covered in User Access Privileges)
- Access to Wayfinder itself can either be at the platform-level or at the workspace-level
- Platform-level access provide access to configurations that operate outside of any workspace (i.e. network plans, cluster plans, cloud access configuration etc.)
- Workspace-level access provide access to the resources that are specific to a workspace (i.e. grant users permissions to deploy applications)
Understanding roles and access policies
A role is a generic set of permissions against Kubernetes resources, for example, clusters. When an access policy is applied to a role, those generic permissions are constrained to specific resources and conditions.
For example, the cluster.admin role has generic permissions to let users do many operations on a cluster. The access policy associated with this role determines:
- Which workspace groups (for example workspace owner or member) can assume this role
- Which cluster(s) the role applies to
- What times of day and days of the week the role can be assumed
- What source networks the user can come from to assume the role
- How long the user can assume this role before it expires
So whether a specific user can assume this role for a specific cluster depends on the access policy.
Workspace groups are a way to include multiple users within an access policy. For example, if you put users in the workspace admin group, they will all be subject to a
policy that refers to the admin group. For details, see:
Manage user roles
About global roles and workspace roles
There are two kinds of roles:
-
Global roles: Wayfinder comes with default global roles, and a Wayfinder administrator can create more global roles.
- Global roles are at the platform level and are available as read-only in all workspaces. They cannot be edited, disabled, or deleted at the workspace level.
- Wayfinder admins can disable or delete any role they create.
- Wayfinder admins cannot delete Wayfinder's default roles, but can disable them.
-
Workspace roles: All global roles are available in workspaces as read-only. Workspace admins can also create their own roles, specific to their workspace only.
See Default roles for a list of roles that come with Wayfinder.
View roles, permissions, and access policies
Use the wf get globalaccessrole command to view the available roles (platform-level). Below shows the default global roles.
➜ ~ wf get globalaccessrole
NAME DESCRIPTION STATUS ENABLED AGE
cluster.admin Full cluster administration Success Unknown 51d
cluster.deployment Provision standard resources for access token deployments to any namespace in a cluster Success Unknown 51d
cluster.deployment-readonly Cluster-wide read access to resources required for namespace deployments using access tokens Success Unknown 51d
cluster.view Read-only access to standard resources, excluding secrets Success Unknown 51d
namespace.admin Full namespace administration Success Unknown 51d
namespace.daemonset Provisioning of daemonsets to a namespace for deployments using access tokens Success Unknown 51d
namespace.deployment Provisioning standard resources to a namespace for access token deployments Success Unknown 51d
namespace.edit Full access to standard resources, excluding secrets read Success Unknown 51d
namespace.troubleshooting Retrieve logs and exec into pods Success Unknown 51d
namespace.view Read-only access to standard resources, excluding secrets Success Unknown 51d
secrets.view View secrets Success Unknown 51d
➜ ~
Use the -w WORKSPACE flag with the wf get accessroles command to see the roles for a specific workspace. The command returns the global roles, because all workspaces inherit them by default.
The CLI command's output also contain all the custom roles that were created at the workspace-level i.e. custom.workspace.role as created in the example's ctest workspace. Custom roles
only exist in the workspace in which they were created.
➜ ~ wf get accessroles -w ctest
NAME DESCRIPTION STATUS ENABLED AGE
cluster.admin Full cluster administration Success Unknown 51d
cluster.deployment Provision standard resources for access token deployments to any namespace in a cluster Success Unknown 51d
cluster.deployment-readonly Cluster-wide read access to resources required for namespace deployments using access tokens Success Unknown 51d
cluster.view Read-only access to standard resources, excluding secrets Success Unknown 3d1h
custom.workspace.role This is an example of a custom role as created at the workspace level Success Unknown 38s
namespace.admin Full namespace administration Success Unknown 3d1h
namespace.daemonset Provisioning of daemonsets to a namespace for deployments using access tokens Success Unknown 3d1h
namespace.deployment Provisioning standard resources to a namespace for access token deployments Success Unknown 3d1h
namespace.edit Full access to standard resources, excluding secrets read Success Unknown 3d1h
namespace.troubleshooting Retrieve logs and exec into pods Success Unknown 3d1h
namespace.view Read-only access to standard resources, excluding secrets Success Unknown 3d1h
secrets.view View secrets Success Unknown 3d1h
➜ ~
Use the wf get accessrole NAME-OF-ROLE -o yaml command to view the manifest of a specific role.
➜ ~ wf get accessrole namespace.deployment -o yaml
apiVersion: policydelivery.appvia.io/v1alpha1
kind: AccessRole
metadata:
name: namespace.deployment
namespace: ws-app
spec:
description: Provisioning standard resources to a namespace for access token deployments
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- events
- persistentvolumeclaims
- persistentvolumes
- pods
- secrets
- serviceaccounts
- services
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- apps
- batch
- coordination.k8s.io
- extensions
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- cronjobs
- deployments
- deployments/rollback
- deployments/scale
- frontendconfigs
- ingressclasses
- ingresses
- jobs
- networkpolicies
- replicasets
- replicasets/scale
- replicationcontrollers/scale
- statefulsets
- statefulsets/scale
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- policy
resources:
- poddisruptionbudgets
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- rbac.authorization.k8s.io
resources:
- roles
- rolebindings
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- apiGroups:
- autoscaling
resources:
- horizontalpodautoscalers
- verticalpodautoscalers
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- acme.cert-manager.io
- cert-manager.io
- helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io
- source.toolkit.fluxcd.io
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
- apiGroups:
- terraform.appvia.io
resources:
- configurations
verbs:
- '*'
➜ ~
To view roles in Wayfinder's web interface:
- For Global Access Policies: Select Admin, and then navigate to Access > Roles
- For Workspace Access Policies: Select Workspaces > Your-Workspace-Name, and then navigate to Settings and select the Roles tab
Workspaces inherit global roles by default. When custom roles are created in a workspace, then the custom role will only exist in the workspace in which it was created.
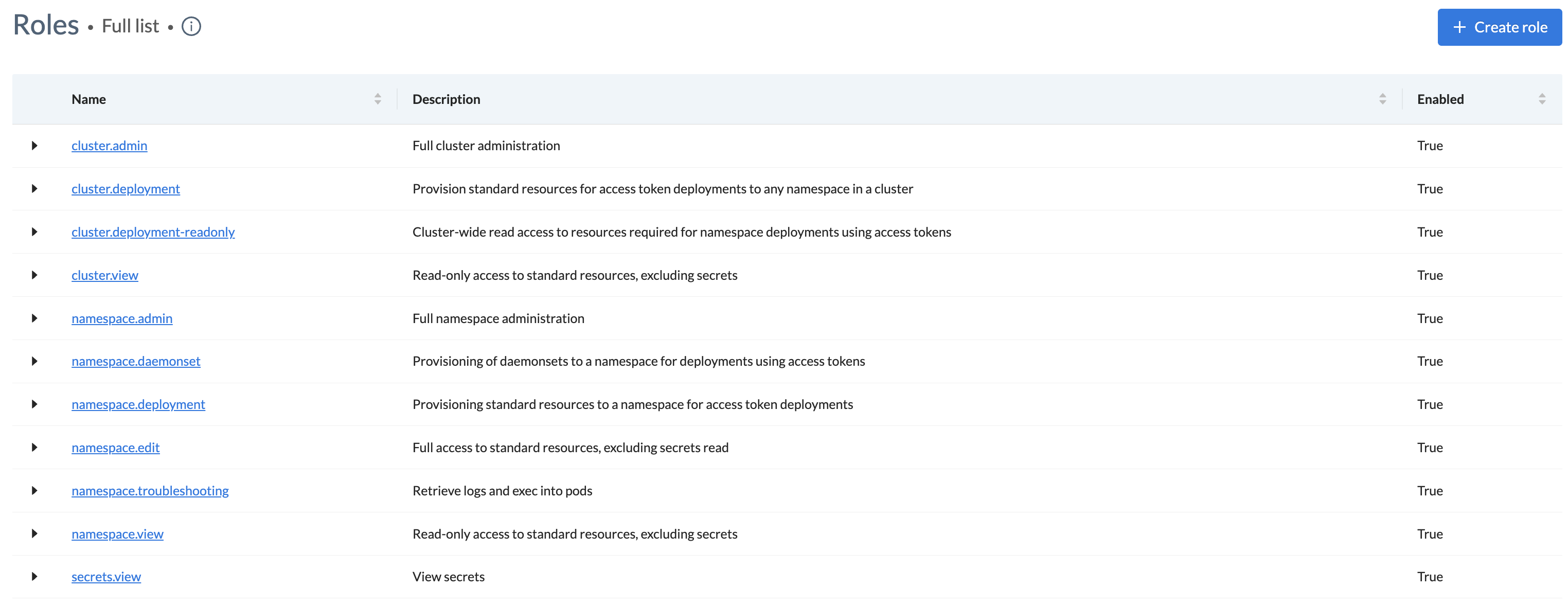
- Click the name of a role to see the permissions that the role provides. Permissions are against Kubernetes resources i.e. clusters that Wayfinder manages.
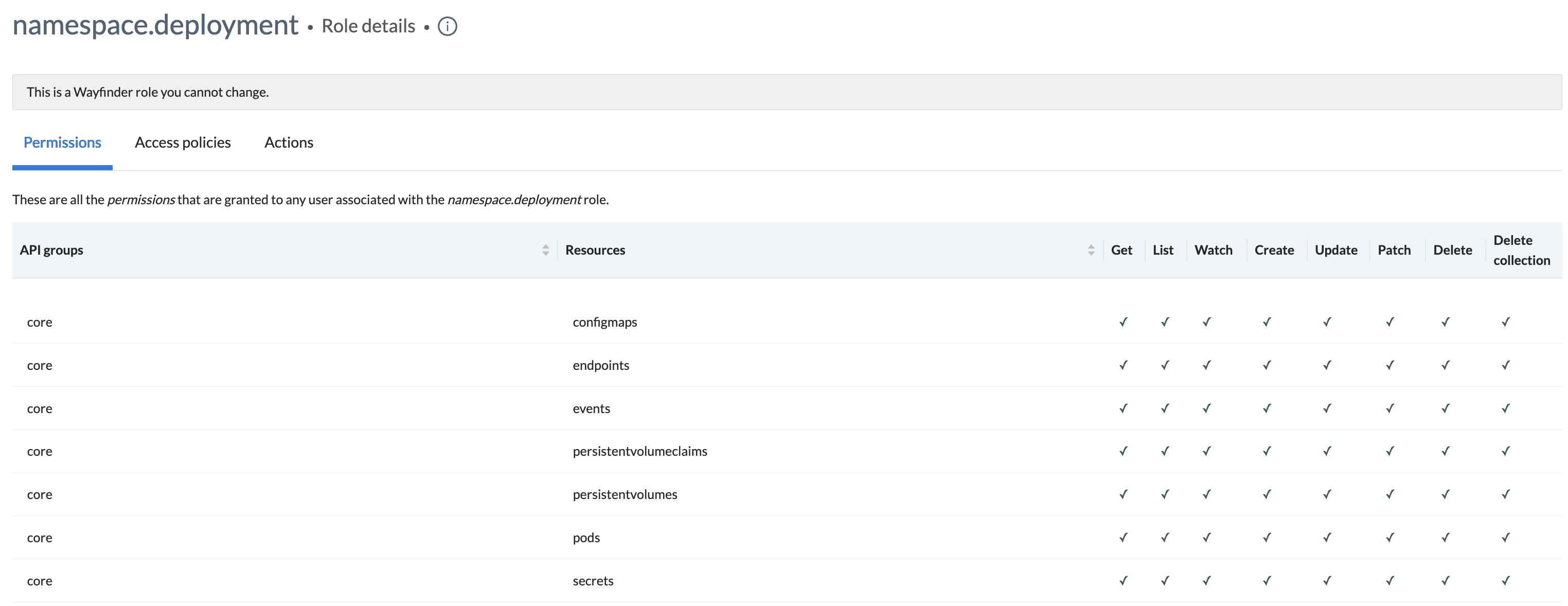
- Click the Access policies tab to see the associated policies with the role.
- Click the Actions tab to see useful CLI commands and manifest files.
Create a role
In addition to Wayfinder's default roles, you can create new ones to suit your needs. You might want a new role, for example, if you need a special permission not covered by the default roles.
Roles created by the Wayfinder admin are global and available to all workspaces. Roles created at a workspace level apply only to that workspace.
To create a new role:
- For Global Access Policies: Select Admin, and then navigate to Access > Roles
- For Workspace Access Policies: Select Workspaces > Your-Workspace-Name, and then navigate to Settings and select the Roles tab
- Click Create Role
- Enter a Name and a Description for the role
- Click on the Add permissions button to add permissions to the role. The sequence is per Group as follow:
- Select a Kubernetes Group
- Add one or more Kubernetes Resources by clicking on all which applies in the drop-down
- Add one or more Kubernetes Verbs by clicking on all which applies in the drop-down. If you have selected more than one resource in the previous step, then all of the verbs will apply to all of the resources. If you want different verbs per resource, then you need to create them separately.
- Once you are happy, you can add more groups and repeat the sequence as outlined above.
- Select the scope for the permissions. You can choose between the Kubernetes Cluster or the Kubernetes Namespace.
- Click Next to see a preview of the permissions in your new role
- Click Back to continue editing
- Click Save to save the role
- If you need a new policy to control access for this role, see Create access policies below.
If you have created a global role, then that role will be inherited by all workspaces. If you have created a workspace role, then that role will only be available in the workspace in which it was created.
Edit a role
You can only edit roles that you have created. The default roles that come with Wayfinder cannot be edited.
When you edit a role, it is updated for anyone who assumes the role after your edits. But current live sessions using this role are not affected.
Enable or disable a role
The Wayfinder and workspace admins have these permissions to disable/enable roles:
- Wayfinder admins: Can enable/disable any role (default or custom), whether it's global or specific to a workspace
- Workspace owners: Can enable/disable only roles they create for their workspaces
Disabling a global role deletes it in workspaces.
To enable/disable a Wayfinder default role:
-
Use one of these CLI commands to enable or disable the role.
-
If it's in a workspace:
wf [enable | disable] accessrole ROLENAME -
If it's a global policy:
wf [enable | disable] globalaccessrole ROLENAME
-
Delete a role
You can delete any role you created. However, Wayfinder default roles cannot be deleted. Instead the Wayfinder admin can disable default roles if necessary.
CLI: wf delete accessrole ROLENAME
Manage access policies
Refer to the following areas to learn more about cluster access policies:
- About global and workspace policies
- View access policies
- Create access policies
- Update access policies
- Enable or disable an access policy
- Delete a policy
Getting access
Wayfinder users get access to roles (and the permissions provided by the roles) in two ways:
-
Human users - Get access to infrastructure via the
wf accessCLI command. For details, see Human Roles. -
Access token - Get access to infrastructure when you create the access token and and assign it a role. The generated access token can be used in your CI pipeline to automate deployments. For details, see Access Tokens.
Revoking access
Administrators can view and revoke live user access sessions. For details, see Revoking Access.
Create Custom Workspace Groups
Custom workspace groups are only available in the workspace in which it has been created. Do not confuse with Wayfinder's default workspace groups which are inherited by all workspaces.
Workspace owners can create custom workspace groups within their workspaces as follow:
- Use
wf create workspacegroupto create a custom workspace group. - Use
wf create workspacegroupmemberto add a user to the custom workspace group.
To create a custom workspace group using Wayfinder's web interface:
- Select Workspaces > Your-Workspace-Name, and then navigate to Settings
- Select the Group tab
- Select the Create Group button
- Enter a name and description for the group
- Select the group members
- Follow the instructions to create Access Policies that provide users in the group access to resources.